Once considered a “beauty buzzword”, collagen has come a long way from being an ingredient added to costly creams that promise youthful looking skin. Here’s what research says about how collagen benefits our entire body.
As the most abundant protein found in animals and the human body, collagen offers much more than a “natural alternative” to Botox (as stated by some celebrities). (1)
When taken as a nutritional supplement, collagen protein has also been shown to relieve digestive issues, build lean muscle mass, boost the immune system and relieve joint pain. (2) And yes: taking collagen protein can significantly improve skin elasticity. (3)
How does bone broth fight inflammation AND promote weight loss? Download our Free Bone Broth Guide And Recipes To Find Out Now!
Click here to get your FREE Bone Broth Guide And Recipes Today!
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is a protein that provides the framework for our bones, muscles, tendons and ligaments. It’s also found in the skin, gums, cartilage and gut. Having a body without collagen would be like building a house without nails. In other words, we’d just be a pile of skin and bones if it weren’t for collagen holding our musculoskeletal system together.
As a protein, collagen is a rich source of several essential amino acids. Amino acids are needed by our bodies for nearly every biological function, including digestion and absorption of nutrients, building muscle, transporting oxygen, and producing neurotransmitters. (4) These amino acids are called essential because our bodies cannot produce them. Instead, we must obtain them from dietary sources. (5) Our bodies cannot produce essential amino acids. We must obtain them through our diet.
The amino acid profile of collagen is why it’s so beneficial when taken as a nutritional supplement. By providing your body with several of the amino acids it requires to function optimally, you’ll be supporting your health on a foundational level. And as a result of consistently receiving several essential nutrients from your diet, you’ll feel a positive difference in your health and be able to perform at your best.
Types of Collagen

You may know that our bodies contain abundant amounts of collagen, but did you know there are actually 16 different types of collagen?
The most abundant types, which make up between 80 and 90 percent of all collagen, are Types I, II, and III. (6) Below, we discuss the difference between these three types so you can determine which is best for you.
Type I
Type I collagen is the most plentiful in your body and is found largely in your skin, tendons, organs, vascular system, and bones. This type is extra-important for skin elasticity and keeping things supple.
The fibers of strong Type I collagen can be stretched easily without breaking – an important part of aging and preserving our skin and body’s ability to move fluidly without “breaking” or tearing. Type I and III collagen benefits are similar, and may often occur together in a supplement for healing your gut lining or minimizing fine lines and wrinkles in your skin. (7)
Type II
Type II collagen is the collagen that makes up cartilage, the strong but flexible substances between our joints and connective tissues. Keeping cartilage strong with enough collagen helps keep our joints healthy and strong. (8)
When this type of collagen degenerates or becomes weak, we can experience joint health issues. This is why it’s common to see Type II collagen in joint health supplements, often alongside glucosamine and other compounds that help promote cartilage health.
Type III
Type III collagen is similar to Type I in that it is present in skin, organs, blood vessels, and even in your heart. People deficient in this type of collagen might experience things like vascular deficiency and other problems with weak blood vessels, such as aneurysms. (9)
Type III collagen can also be used to help heal the gut lining, as it’s similar to Type I and is often found with Type I in supplements. Research shows it can be found in abundance in skin layers as well, which makes it great for combating aging and keep the skin supple. (10, 11)
3 Natural Sources of Collagen

Collagen supplements are all the rage nowadays, but you can actually get quite a bit of collagen naturally from certain foods.
1. Bone Broth
Bone broth is broth made from animal bones, mainly beef and chicken, that contains ample amounts of collagen. Aside from an abundance of Type I collagen, bone broth also contains anti-inflammatory amino acids like glycine. Chicken bones or carcasses may also contain more Type II collagen due to the connective tissue on the carcass. (12, 13, 14)
Try adding bone broth to your diet three to four times a week. You can either sip it plain or use it as a stew or soup base.
2. Fish
Fish also contains collagen, mostly in the form of Type I. If you reach for fish that contains the bones and skin, such as sardines and skin-on salmon, you’ll get an even higher dose. (15)
Along with its abundant omega-3 fatty acid content, fish makes a great choice for getting a dose of healthy fats and skin-loving collagen.
Grill, bake, or roast your favorite wild-caught fatty fish at least three times a week. Have it as a main for dinner, or even top your salads with it for lunch.
3. Eggs
Eggs are another common food that contains collagen. You’ll find mostly Type I collagen throughout the whites and shell. They also contain plenty of amino acids that play a role in keeping the joints and skin healthy. (16)
Give eggs a go any time but, of course, know that they make an excellent breakfast choice. Scramble them up with some sweet potato hash, or have a couple over-easy with a half an avocado.
Collagen Nutrition Facts
Collagen is made of 1,050 amino acids, which are wound around one another to form a triple helix arrangement. The most abundant of these amino acids is proline, glycine, and hydroxyproline.
All three amino acids work together to form the collagen structure. L-proline is utilized by your body to produce hydroxyproline, where together they form the backbone of collagen to stabilize its structure. Glycine then assists in “gelling” together the collagen triple helix. (17, 18)
Collagen and its amino acids have minimal calories by themselves, so the calorie content will depend on what you consume to get it. Most foods with collagen also contain abundant amounts of protein and some fat. If you take a collagen supplement, it will most likely contain protein and a small number of calories as well. (19, 20)
Recipes to Try
These recipes will get you started on collagen-rich dish ideas. From DIY bone broth to skin-on fish and egg recipes, they’re the perfect easy way to get a daily dose.
- Gut-healing bone broth
- Tripe, bacon, and bone broth gut-nourishing stew
- Fisherman’s eggs
- Salmon eggs benedict with sweet potato “muffins”
- Crispy-skin fish and mashed cauliflower drizzle with oregano butter
Collagen Protein vs. Collagen Peptides

When it comes to taking collagen as a nutritional supplement, there are two different forms of collagen you can take: collagen peptides and collagen protein.
While both varieties of collagen offer similar amino acid profiles and health benefits, there are subtle differences between the two – mostly in terms of digestibility and how to add it to your diet.
Collagen Protein
Collagen protein is also called gelatin. It is made by cooking, and then drying, collagen before processing it into a powder.
The main factor that sets collagen protein apart from collagen peptides is that it gels when mixed with a cold liquid. For this reason, collagen protein is an ingredient for replacing glutenous thickeners in soups, broths and gravies. Based on the gel-like consistency of collagen protein, it can also be used to add extra protein to omelets and Paleo desserts such as mousses and coconut milk ice cream. Collagen protein turns gelatinous, while collagen peptides don’t.
Collagen protein also takes longer to digest than collagen peptides. For this reason, collagen protein has been studied for its therapeutic use in specialty diets (such as the GAPS diet), which aim to reduce intestinal inflammation and heal leaky gut. (21)
Collagen Peptides
Collagen peptides are processed differently than collagen protein, or gelatin. Instead of just being cooked, dried, and ground into a powder, the amino acids in collagen peptides also get broken down during processing and are said to help enhance digestibility.
Collagen peptides have a different consistency than collagen protein. Since the amino acids are broken down during processing, collagen peptides do not gel when mixed with liquids. Therefore, they blend well with beverages, hot and cold alike. Collagen peptides can be added to your favorite juice or smoothie recipes and make a mean Paleo protein pancake batter. You can even add collagen peptides to your hot, frothy butter coffee.
Both collagen peptides and collagen protein contain very similar amino acid profiles, so you don’t have to worry about receiving fewer nutrients by choosing one variety over the other. Instead, the type of collagen you use will depend more on your current state of health (i.e., a compromised digestive system) and the preferences in temperature and texture of your recipes.
6 Amazing Collagen Benefits

Now that you understand the difference between collagen protein and collagen peptides, let’s take a look at the other ways collagen can help improve your health.
1. Curbs Cravings
If you suffer from sweet cravings, it’s not your fault. Whether they’re mild, intense, frequent or rare, cravings for sugary foods are often the result of blood sugar fluctuations.
You see, protein is the macronutrient our bodies require to keep blood sugar levels stabilized. (22) So, when we don’t receive an adequate supply of high quality protein in our diets, our blood sugar levels are at a greater risk of becoming imbalanced.
Blood sugar is directly related to your energy levels. Therefore, when blood sugar levels spike and crash – which is often due to eating excess sugar, going long periods of time without eating, mental stress and a lack of protein – our bodies will crave fast digesting carbs to get our blood sugar and energy levels back up.
As you can see, balancing blood sugar levels can be extremely helpful when it comes to kicking sugar cravings (not to mention preventing future blood sugar conditions down the road, such as type 2 diabetes). The best way to balance your blood sugar levels is by adding more protein to your diet – and collagen is an ideal way to do so.
2. Easy Way to Increase Protein Intake
Could there be an easier and more delicious way to increase your protein than by eating Paleo pancakes or chocolate mousse? Didn’t think so.
Making your favorite Paleo recipes with the addition of collagen is not only an easy way to improve the texture of your recipes, but also a convenient way to increase the nutritional value with minimal effort.
3. Healthy Alternative to Meat
Organic, grass-fed meat is the preferred type of protein on a Paleo diet because it has a higher omega-3 content and isn’t raised with growth hormones and antibiotics. But in some cases, grass-fed meat isn’t always affordable or easily accessible.
Unfortunately, factory-farmed meat isn’t an ideal alternative. Factory-farmed animals are typically raised with growth hormones such as rBGH and fed a diet high in corn and grains. Additionally, animals that are fed a corn and grain diet are low in omega-3’s and high in omega-6’s. (23) Omega-6’s are a pro-inflammatory fatty acid, which can cause inflammation in the body when consumed in excess. (24)
Therefore, a high quality collagen protein from grass-fed, pasture-raised animals can provide a safe, healthy and low-cost alternative to meat.
4. Improves Digestion
As mentioned above, collagen may be helpful for relieving the intestinal inflammation associated with food sensitivities and digestive disorders, such as leaky gut. (25) This is why collagen peptides are recommended for those who follow anti-inflammatory diets, such as the GAPS diet.
5. Reduces Inflammation in Joints
Collagen peptides also reduce inflammation in the joints. It’s great for patients with osteoarthritis, and can relieve joint pain in athletes. (26)
6. Hydrates Skin
One study showed that taking collagen peptides for 8 weeks resulted in a significant improvement in skin hydration and skin collagen production. This suggests that taking collagen peptides can promote visible improvements in the skin’s appearance with only a few weeks of supplementation. (27)
How to Find a Quality Collagen Supplement
As suggested above, the quality of the collagen you choose is extremely important. Choose collagen products the exact same way you’d choose meat.
Start by looking for a quality collagen supplement sourced from pasture-raised, grass-fed cows that haven’t been raised with growth hormones (such as rBGH).
We recommend Vital Proteins for a top-notch collagen brand. They formulate their collagen peptides and gelatin from grass-fed cows in Brazil, where it is against the law to inject cows with growth hormones. When buying collagen supplements, make sure it’s non-GMO and allergen-free.
A quality collagen supplement should be Non-GMO and free of common allergens such as soy, corn and gluten. It’s important to avoid collagen supplements that contain added sugar, sweeteners, binders, fillers and artificial colors and flavors.
Lastly, your collagen supplement should be packed in an air-tight container to help prevent moisture from entering. Collagen absorbs moisture very easily, which allows bacteria to break it down and degrade it. Your collagen container should always be BPA-free to keep it clear of endocrine disruptors. (28)
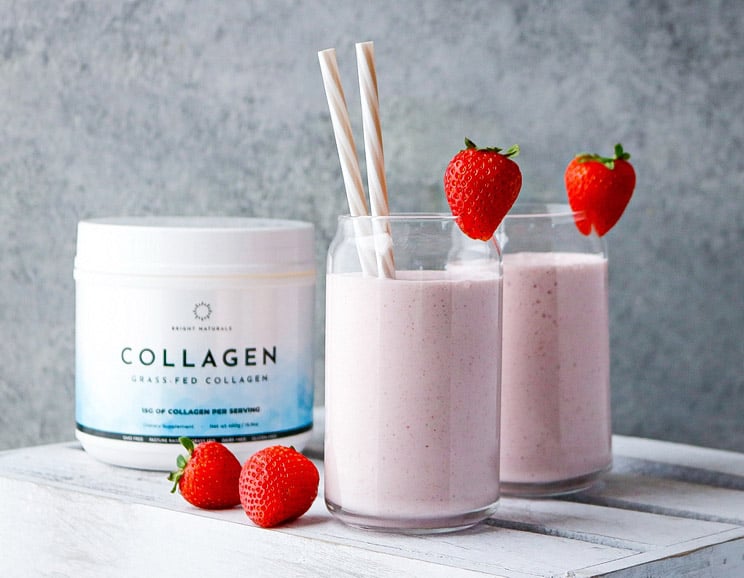
Personally, we recommend Bright Naturals Collagen because it meets all of the above quality requirements, and then some.
How to Cook, Bake and Drink Collagen
Try adding collagen to all of your favorite recipes, from gravy to dessert. It’s safe to cook and bake with it since collagen’s nutritional value doesn’t change when it’s exposed to high temperatures. You can also mix it into your favorite beverages.

Cook It:
The best form of collagen to cook with is collagen protein because it gels when mixed with liquid. This makes collagen protein an ideal healthy thickener that can be used in all kinds of recipes.
Cooking with collagen protein (gelatin) is easy. All you have to do is mix the collagen protein with a hot liquid until it begins to dissolve. Let it cool for about 5-10 minutes, then add to your favorite recipes.
Use collagen protein in things like gravies, soups, Paleo gummy bears, jello, puddings or marshmallows.
Bake It:
Use gelatin as an egg replacement in recipes by mixing 3 tablespoons of hot water with 1 tablespoon of gelatin (which replaces 1-2 eggs).
Collagen peptides are also safe to cook and bake with. They don’t gel when combined with a liquid, so they can be easily mixed into any recipe without dramatically changing the texture. Try it in grain-free brownies and Paleo protein bars.
Drink It:
Collagen peptides blend well and add a creamy texture to any juice, smoothie or protein shake recipe. Use it as an alternative to protein powder!
Needless to say, adding collagen protein and peptides to your diet makes it easy to provide your body with the extra boost of nutrition it’s looking for to help ensure a full and vibrant life.
(Read This Next: How to Buy the Best & Healthiest Coconut Oil)


 Baked Eggplant Caprese Stacks
Baked Eggplant Caprese Stacks








Show Comments