MCT oil is one of the fastest sources of energy available – and no, MCT oil isn’t coconut oil. Here’s how to supplement with MCT oil to fuel your body and brain.
If you’ve been visiting your local health food store lately, you’ve probably come across MCT oil. While it looks suspiciously like coconut oil, this supplement is much more than a simple culinary oil. Read on to discover what it is and its benefits.
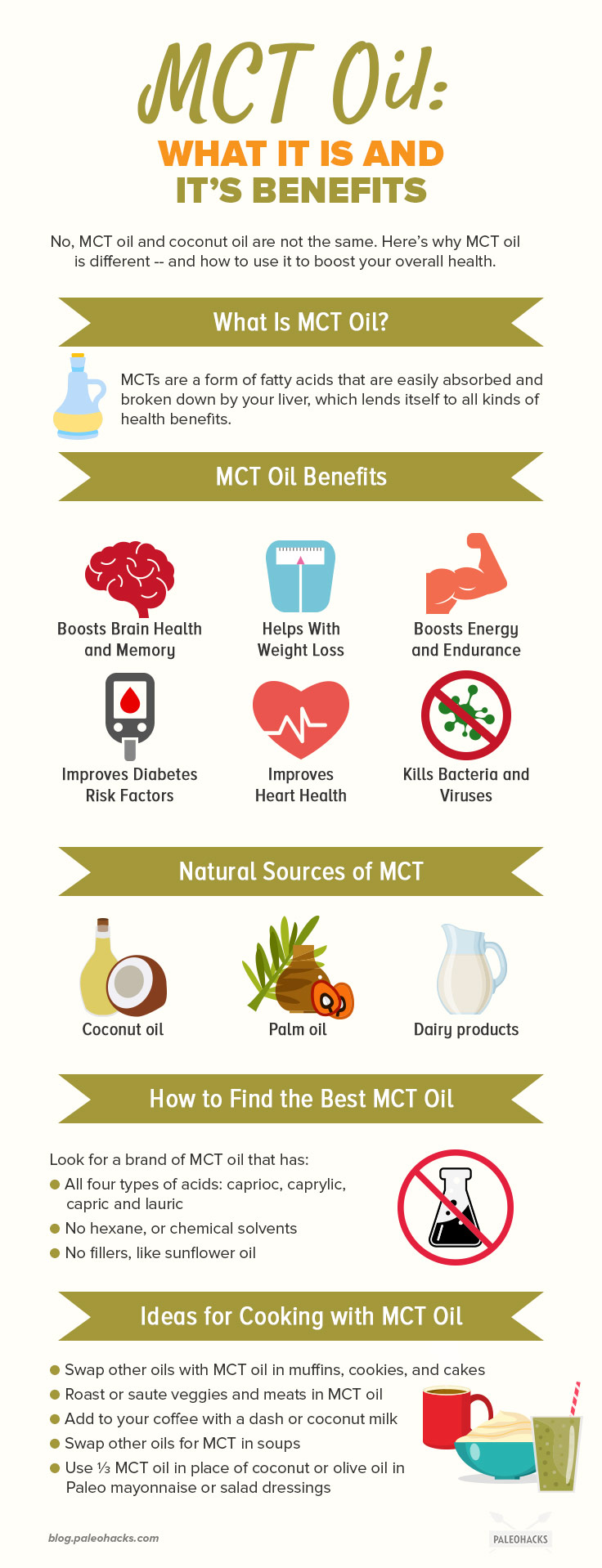
What Is MCT Oil?
Medium-chain triglycerides, or MCTs, are a form of fatty acids found in certain foods like coconut oil and palm oil. MCTs are different from other types of fat because their chemical makeup is balanced in a way that makes them easier to absorb and break down. MCTs are also smaller than other fat particles, allowing them to be absorbed and used more efficiently by your liver. (1)
Can you spare 10 minutes a day? Then you can do this 7-Day Paleo Weight Loss Bodyweight Workout Challenge!
Click here to get your FREE copy!
MCTs unique ability to be absorbed more efficiently gives it numerous health benefits – which is probably why you’ve seen an explosion of it recently in health food stores and online as a “superfood” that can help with anything from brain health to weight loss.
MCT oil is colorless, odorless, and stays liquid at room temperature, which makes it ideal as a supplement to add to certain foods and dishes.
Different Types of MCT Oil

There are four forms of MCTs: caproic acid, caprylic acid, capric acid and lauric acid.
The main difference between these different types is how they behave in your body. Caproic, caprylic, and capric acids go straight to your liver to be used for energy, instead of being absorbed in the small intestine and potentially stored as fat. This is why MCTs are reputed to be great for boosting energy and assisting with weight loss.
Laurie acid is different from these other forms in that it is slower to absorb. Both lauric and caprylic acid are highly antimicrobial as well. (2)
How is MCT Oil Different From Coconut Oil?
Some people confuse coconut oil for MCTs, but they aren’t the same thing. While coconut oil is one of the most abundant sources of MCTs, MCT oil is a concentrated form of all four MCTs.
Additionally, while coconut oil contains MCTs, it does so in a different ratio than MCT oil. Coconut oil is mostly abundant in lauric acid (about 50 percent), while MCT oil contains more of the other three types of MCTs than coconut oil. This is one of the reasons many believe MCT oil is a superior source of MCTs than coconut oil, since the other types of MCTs can be more difficult to get from foods in a balanced ratio.
6 MCT Oil Benefits

Research has exploded lately on the benefits of MCTs. Check them out below.
1. Boosts Brain Health and Memory
Studies show that MCTs help improve cognition and boost memory. This is because MCTs produce ketones, and when they reach your liver, they act as an alternative energy source for your brain.
One major study in particular found that MCTs improved learning, processing, and memory in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, with another showing MCTs improved cognition in diabetics with hypoglycemia. (3, 4)
2. Helps with Weight Loss
The fact that MCTs are transported directly to your liver to be used as fuel instead of stored as fat has spurred on the theory that they may help promote weight loss by encouraging your body to burn fat as fuel.
Studies show there is some merit to this, finding that MCT oil supplementation has been able to increase the calories and fat burned in participants. (5) In addition, another study found that MCTs can increase the hormones that reduce appetite and encourage the feeling of satiety. (6)
3. Boosts Energy and Endurance
Many people supplementing with MCT oil claim it provides a boost of energy and increases endurance during their workouts. Considering the rapid transformation of MCTs by the liver into energy, it makes sense you could get a nice boost of energy from ingesting them.
One study found that athletes consuming food rich in MCTs, rather than longer-chain fats, improved the time they could endure high-intensity exercise. (7)
4. Improves Diabetes Risk Factors
While the mechanism for exactly how this works is unknown, studies show that MCT oil can help improve risk factors for diabetes, such as insulin resistance, obesity and cholesterol. (8)
5. Improves Heart Health
Studies show that MCTs can help prevent the development of metabolic syndrome – a group of symptoms including obesity, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance. (9) This group of symptoms is directly linked to the development of cardiovascular problems and disease, so consuming MCTs could help lower your risk of heart trouble by preventing metabolic syndrome.
6. Kills Bacteria and Viruses
Lauric and caprylic acid (both types of acids found in MCT oil) have been shown to be potent antibacterials and antimicrobials that can help combat anything from candida to yeast. These acids work by disrupting the cell membrane of bacteria, leaving them susceptible to your body’s immune system. (10)
Natural Sources of MCT

After coconut oil, palm oil is the second best source of MCTs. Dairy products like cheese, milk, butter and yogurt also have high concentrations of MCTs. However, since most of these products are not Paleo, we recommend sticking with grass-fed butter as your only dairy-related source of MCT oil (if you can tolerate it).
MCT Oil Nutrition Facts
1 tablespoon of MCT oil contains:
- 125 calories
- 14 grams of fat
- 14 grams of saturated fat
- 0 grams of carbohydrates
- 0 grams of cholesterol
How to Find the Best MCT Oil
The key to finding a high-quality MCT oil is to research the extraction process of each brand before you buy. Many companies will use hexane or other chemical solvents to extract MCTs from coconut oil, which could potentially contaminate the product. Check a brand’s website for clearly-stated manufacturing processes.
Another thing to look for when buying MCT oil is the ratio of the four types of acids in the product: caproic acid, caprylic acid, capric acid, and lauric acid. Make sure these aren’t cut with any fillers, like sunflower oil.
How to Use MCT Oil (As a Supplement, in Cooking, etc.)

MCT oil can be used in nearly every recipe that requires a liquid. Think smoothies, soups and stews. You can even blend some up into homemade salad dressings!
Below are a few ideas:
- Use MCT oil in place of coconut or olive oil in baking recipes, such as muffins, cookies, and cakes.
- Roast and/or saute veggies and meats in MCT oil in place of coconut or olive oil.
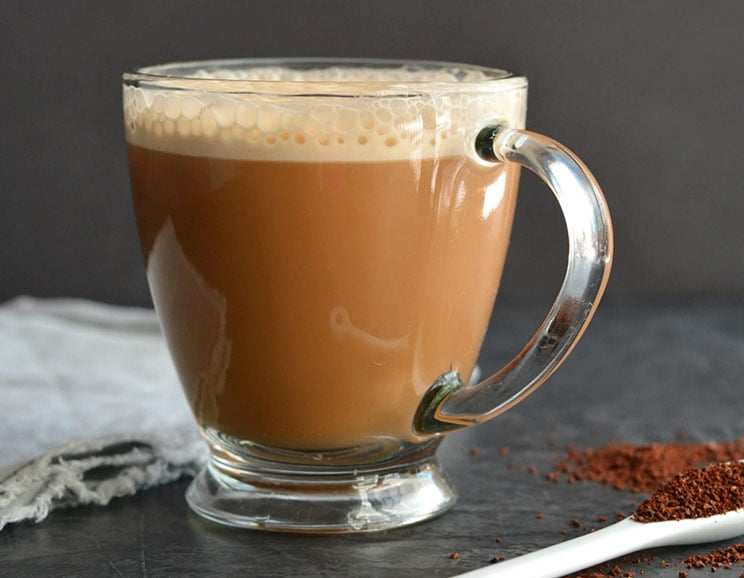
- Add MCT oil to your coffee along with a dash or coconut or almond milk for a brain-boosting morning cuppa.
- Add MCT oil to smoothies or soups in place of other oils.
- Create homemade dressings, such as Paleo mayonnaise and salad dressings, by using ⅓ MCT oil in place of coconut or olive oil.
(Read This Next: The Benefits of MCT Oil vs Coconut Oil)


 Signs of Diastasis Recti + 3 Ways to Naturally Fix It
Signs of Diastasis Recti + 3 Ways to Naturally Fix It









Show Comments