Know how to recognize the signs of brain inflammation and discover which keto foods to eat for better brain health.
Inflammation in the brain is an often silent problem that goes on for a long time, causing untold levels of damage to the nervous system and other body systems.
Scientific research is uncovering more about the causes of brain inflammation and the conditions that are related to it, such as dementia and Alzheimer’s – sometimes referred to as type 3 diabetes.
Curious about ketosis?
Click here to get the FREE Easy Keto Guide to learn the right way to go keto!
Eating to live an anti-inflammatory lifestyle is essential for health, but we can’t assume that inflammation only shows up in joints or the digestive system. We must focus on understanding the symptoms of excess inflammation in the brain and work to live a preventive lifestyle.
What Causes Inflammation In the Brain?

Inflammation gets a lot of buzz in the Paleo and health worlds because it can contribute to so many ailments and chronic health problems. The brain is not immune to inflammation, but research is only recently starting to delve into what happens when the brain gets inflamed.
Brain tissue is delicate, and inflammation, either short-term or long-term, can have some serious results, ranging from anxiety and depression to Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and dementia.
While brain trauma can contribute to inflammation, you don’t have to incur a head injury to be affected. Anything that leads to systemic inflammation can cause inflamed tissues in the brain. How we develop brain inflammation is partially determined by our genetics – certain people can be predisposed to thyroid disorders or arthritis, while others can have a tendency toward experiencing brain-related problems like Alzheimer’s.
Beyond genetics, other factors that can lead to inflammatory problems in the brain, systemically, or elsewhere, include: (1, 2, 3)
- Pathogens
- Allergens
- Infections
- Chronic stress
- Lack of exercise
- Inflammatory foods
- High blood glucose
- Excess weight and obesity
All of these various problems can lead to an overproduction of cytokines, which are chemical messengers that regulate inflammation. Cytokines turn on other specialized cells in the brain that, once activated, can remain in a cycle of “on,” perpetuating brain inflammation, leading to cellular damage, brain fog, reduced brain function, and mood disorders. When this process continues unchecked for months and years, disorders like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and dementia can begin. (4) [tweet_quote]Brain tissue is delicate, and inflammation can have some serious results, ranging from anxiety and depression to Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and dementia.[/tweet_quote]
So, how are some people profoundly affected by them while others are not? Genetics do play a role, but another element is the gut. A large portion of the nervous system, known as the enteric nervous system, resides in the gut and millions of neurons connect the enteric nervous system to the brain. When inflammation is present, from conditions like leaky gut or other microbiome disturbances, this can influence the inflammation levels in the brain.
The blood brain barrier, referred to as the BBB, surrounds the brain and is meant to keep toxins and other particles out, much like the intestinal wall is meant to prevent any foreign particles from entering the bloodstream in the first place. While both of these are amazing protective mechanisms, both can also become weakened and damaged by the presence of allergens, toxins, and inflammation. (5, 6) When the BBB fails to fully protect the brain, it can become susceptible to damage from excess cytokines and even too much exposure to glucose. Inflammation can even lead to the faster death of brain cells, with an impaired ability to generate new ones. (7)
Bottom line: The brain is protected by a barrier, but numerous factors can weaken it and allow the brain to be exposed to inflammation. The result of this inflammatory exposure can lead to short-term mental disorders or mood problems, as well as long-term problems.
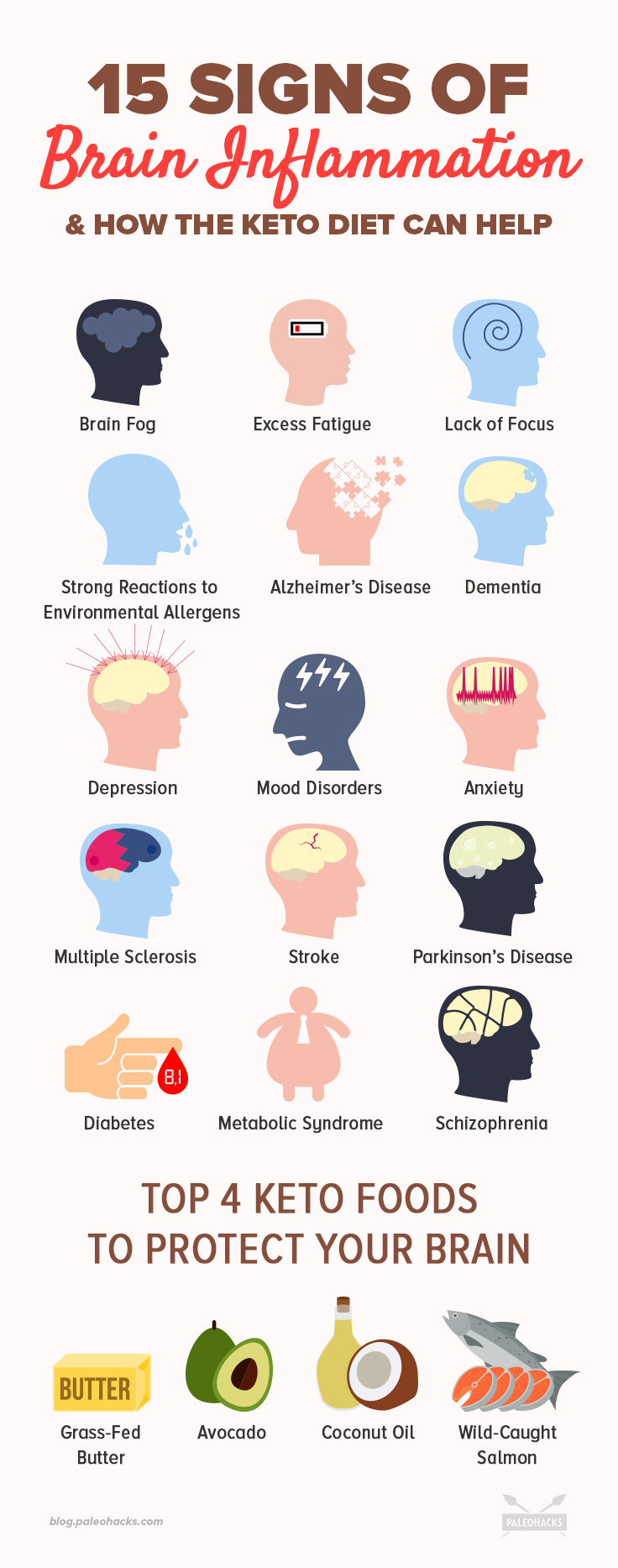
15 Signs of Brain Inflammation

How do you know if you’re dealing with inflammation in the brain? While there aren’t characteristic symptoms that everyone will experience, the following can be clues:
- Slow mental processing or feeling foggy in the brain
- Excess fatigue or always needing caffeine to “wake up”
- Lack of focus or a short attention span
- Strong reactions to environmental allergens or toxins like artificial fragrance, secondhand smoke, pollution, or other chemical smells
Conditions associated with chronic brain inflammation can include: (8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13)
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Dementia
- Depression
- Mood disorders
- Anxiety
- Multiple sclerosis
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome or pre-diabetes
- Schizophrenia
While not everyone who has brain inflammation will develop one or more of these conditions, having an inflamed brain can be a risk factor when paired with other genetic tendencies.
Bottom line: Brain inflammation has specific symptoms and conditions associated with it that can be short-term or long-term. While genes play a role in who will get these conditions, it’s important to understand the inflammation connection to these conditions.
How Keto Reduces Brain Inflammation & The 4 Best Keto Foods for a Healthy Brain
One of the recent breakthroughs in research indicates that a ketogenic diet may be beneficial in reducing inflammation in the brain, helping to reverse or treat certain related conditions. Keto reduces brain inflammation by blocking glucose metabolism, which is a primary cause of inflammation in the brain in the first place. (14)
While glucose is the primary fuel for most people, certain people can become sensitive to it, and in today’s modern culture, many people are chronically overexposed to glucose and have levels higher than our bodies are designed to handle. This continued overexposure for years and even decades can, for some, lead to the breakdowns that cause Alzheimer’s, dementia, and even Parkinson’s disease. (15) [tweet_quote]A ketogenic diet may be beneficial in reducing inflammation in the brain, helping to reverse or treat certain related conditions.[/tweet_quote]
A ketogenic diet consists of plenty of healthy fats and limited amounts of carbohydrates. These four keto foods are not only great for maintaining a healthy keto food plan, but also for nourishing brain health and reducing inflammation.
1. Grass-fed Butter
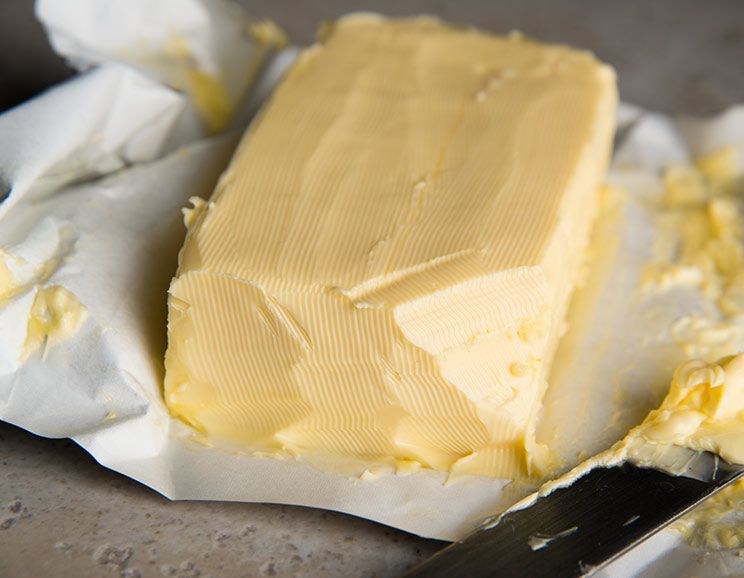

Grass-fed butter is rich in healthy fats and butyric acid, a nutrient which can help to reduce glucose and reverse inflammatory damage from excess levels. (16,17)
To receive the full health benefits of butter, it is essential to ensure that it’s grass-fed and of high quality since conventional butter doesn’t contain the same fatty acid profile.
2. Avocado
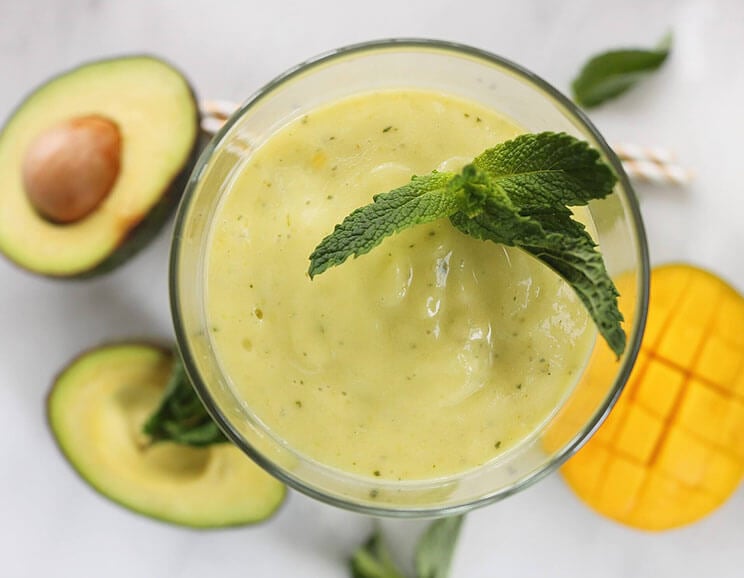

Avocados are keto superfoods thanks to their high concentrations of healthy fats while also containing vitamins and minerals that can be harder to find on a low-carb keto diet. They contain monounsaturated fats that can help to prevent and balance oxidized cholesterol, an inflammatory marker that can be associated with brain inflammation and other risks like stroke and Alzheimer’s. (18)
3. Coconut Oil

Coconut oil is also a keto superfood thanks to the presence of medium chain fatty acids, which can be converted by the liver into ketones for fuel. It can help reduce insulin and glucose and reduce inflammation in the brain. (19) Coconut oil also helps to reduce body fat and facilitate weight loss, both with or without a ketogenic diet. (20, 21)
4. Wild-Caught Salmon

While several fish varieties are rich in nutrients, wild-caught salmon contains the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids, a potent anti-inflammatory nutrient. (22) Eating high quality salmon and other fatty fish can even slow cognitive decline and reduce the signs of aging, all of which work together to provide a healthy brain environment. (23)
Bottom line: The ketogenic diet is therapeutic for many reasons, and one of the primary benefits it can accomplish is to reduce inflammation throughout the body and in the brain. It also reduces an excessive glucose burden while improving the function of the blood brain barrier.
(Read This Next: The Inflammation-Depression Connection)


 9 Easy Wall Stretches for Tight Hips
9 Easy Wall Stretches for Tight Hips







Show Comments