Hair and skin feeling lackluster? Biotin, a little known B vitamin, might be your secret weapon to restoring their natural glow.
Previously known as “vitamin H” due to its powerful influence on hair and scalp health, biotin has since been renamed vitamin B7.
This B vitamin sends energy to cells and has some pretty amazing benefits for your health. Biotin influences the nervous system, and might soon be used as a progressive method to treat multiple sclerosis. (1)
Want naturally radiant skin? We’ve created a FREE guide to give you the best tips & tricks for natural skincare.
Click here to get your FREE copy of our Skincare Guide!
The impressive benefits of this nutrient might be enough to convince you to add it to your shelf of supplements.
What is Biotin?
Biotin is a water-soluble B vitamin, also referred to as B7. Since water-soluble vitamins do not get stored in fat tissues, they get depleted quickly and must be regularly supplied through dietary sources.
This B vitamin hasn’t been researched as much as B12, riboflavin, and thiamine. This is because symptoms of biotin deficiency result in more frustratingly subtle issues, like lackluster hair, skin, and nails, along with nerve irritation and mood problems. While these might not seem extreme, low levels can have a dramatic impact on our personal appearance and how we feel in our own skin.
Symptoms of Low Biotin

The average recommended daily intake for biotin is 5 micrograms for infants and small children, 30 micrograms for adults, and 35 micrograms in pregnant and breastfeeding women. While true deficiency is rare, it’s possible to be low on the daily intake and still notice symptoms.
Common symptoms of low biotin levels might include: (2)
- Dry, itchy, or red skin
- Face rash
- Pink-eye
- Brittle hair or hair loss
- Low energy levels or fatigue
- Digestive problems
- Muscular aches, joint pains or nerve damage
- Seizures
- Mood changes
- Tingling in extremities
- Cognitive decline or impairment
5 Key Benefits of Biotin
Without enough biotin, the body is short on energy. Here are five of the biggest benefits of making sure you get enough.
1. Healthy Hair, Nails, and Skin

The quality of your hair, skin, and nails are a direct reflection of the body’s internal health. If your hair feels dry, your skin is dull, and your nails are brittle, you can help correct them with biotin. (3, 4) In particular, supplementation can improve nail thickness and reduce flimsy, peeling problems. (5)
Research also shows that preventing deficiency in biotin can help protect against hair loss. (6) Make sure you’re getting enough to keep your hair healthy.
2. Helps Manage Type 2 Diabetes
While type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune driven attack of the pancreas, type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disease where insulin and blood sugar regulation cease to function effectively.
Biotin is studied as a way to help control blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. It’s been theorized that people with type 2 diabetes have lower levels initially, which might contribute to metabolic dysfunction in the first place. (7)
While biotin alone can’t improve glucose levels, compelling research shows that when paired with another supplement – chromium – the combination can work to reduce blood glucose levels. (8, 9)
3. Better Digestion and Nutrient Absorption

Biotin is part of a group of enzymes that help the digestive system do its job – basically, it helps the body make glucose (blood sugar) and digestible fat from the foods that you eat. Without enough biotin, your body won’t be able to fully break down fats, carbs, and proteins during digestion, which can set off a chain reaction that leads to other nutrient problems because the body can’t use the vitamins and minerals from the foods you eat.
Biotin helps pull glucose from non-carb foods, like meats and other proteins, in a process known as gluconeogenesis. This is important for the body to be able to make the most out of the food that it takes in while also being able to supply a constant stream of blood sugar to keep the body in balance.
4. Boosts Thyroid Health
Thyroid disease causes a host of body-wide symptoms that can become a full-time job to manage. Between body aches and low energy levels, the final straw for most thyroid patients is the hair loss.
In addition to encouraging hair growth, biotin gives the body healthy hemoglobin and blood. Because the thyroid requires iron to make hormones, if the body is inefficient at transporting nutrients through the body or low in critical nutrients, like iron, thyroid hormones will be too low. This is why biotin is a vital part of supporting a healthy thyroid at a cellular level. (10)
5. Nervous System Support
One of the major diseases that affect the nervous system is multiple sclerosis or MS. It’s driven by an autoimmune attack of the myelin sheath, which covers and protects nerve fibers in the brain, spinal cord, and eyes. Biotin is an essential element for producing the myelin sheath and is currently being researched as a treatment for progressive MS. (11, 12)
Even if you don’t have MS, ensuring you’re not deficient in this crucial nutrient is a great way to protect your neurological health.
How to Safely Supplement With Biotin

Since deficiencies are not common, do you really need to take it as a supplement?
In short, supplementing should be at the discretion of your doctor. If you regularly get lab tests to monitor certain chronic conditions, like thyroid disease, speak to your doctor before starting a supplement. Too much of it can falsely elevate thyroid test results, so even if you are taking a supplement, you may need to take a break for a few days before a doctor’s visit.
Like most B vitamins, biotin works best with the total B-complex family and shouldn’t be supplemented on its own without a doctor’s direction.
Natural Sources of Biotin
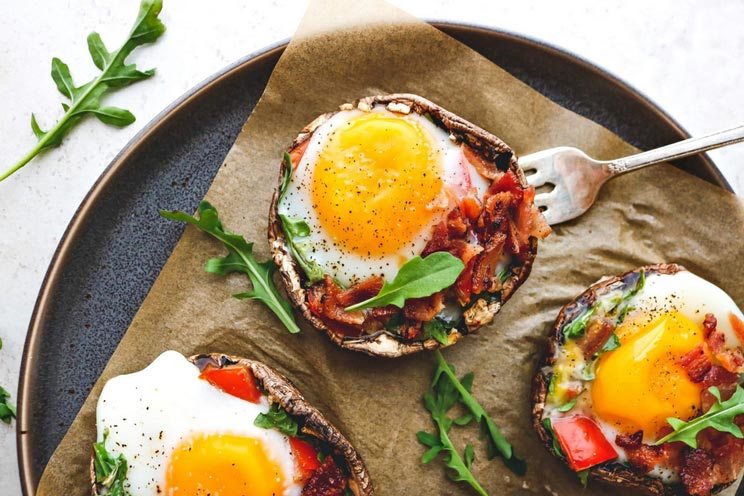

Your microbiome creates a small amount of biotin itself, though not enough to supply the body with its optimal amount. Here are the top Paleo sources:
- Offal, especially liver and kidney
- Yeast
- Nuts and nut butters
- Egg yolks
- Leafy green vegetables
- Cauliflower
- Mushrooms
Bottom Line
It’s not common to be completely deficient in biotin, but many people do run low on this vital nutrient. Biotin supports energy levels, healthy blood, and can even help balance glucose levels. If you don’t regularly eat foods rich in this vitamin, ask your doctor whether supplementation might be right for you.

(Read This Next: Why Do I Need Vitamin B and How Do I Know If I Have a Deficiency?


 Coconut Flour Cinnamon Sweet Potato Bread
Coconut Flour Cinnamon Sweet Potato Bread









Show Comments