There are 11 different types of omega-3 fatty acids, but not all are created equal.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid, and each plays a different role in our health. The top three significant omega-3’s include alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). ALA mainly comes from plants, while DHA and EPA are found in animal fats and fatty fish, like salmon.
DHA in particular is needed for learning ability and brain development, both in infancy and as we get older. Here are even more reasons that DHA is necessary for a healthy body and brain – and how to get more of it in your diet.
Fight inflammation and create easy, healthy meals! We've created a FREE 7-Day AIP Meal Plan
Get Your FREE 7-Day AIP Meal Plan here.
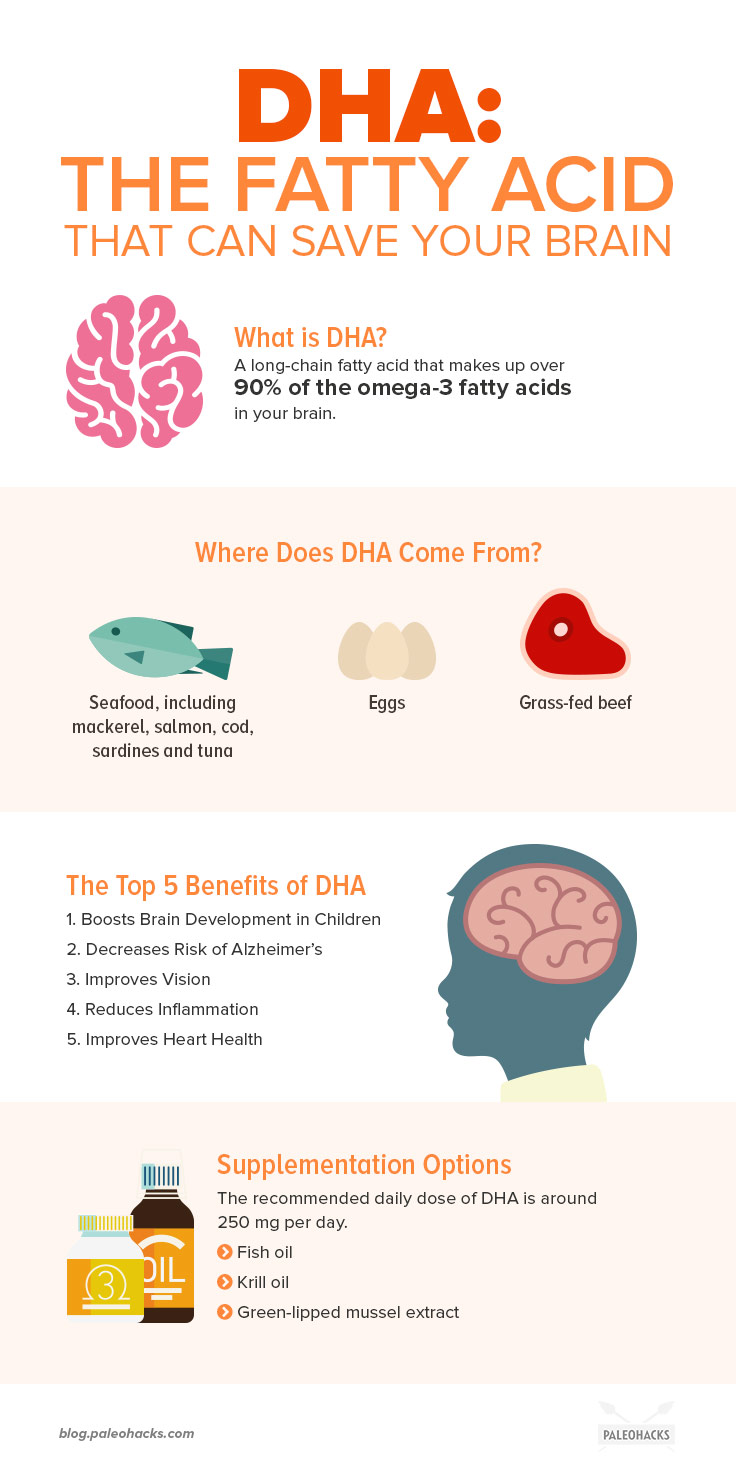
What Is DHA?
DHA is a long-chain fatty acid found in seafood and animal fats. This important structural fat can be found in every cell of your body, and it makes up over 90 percent of the omega-3 fatty acids found in your brain. (1)
Since you cannot produce enough of it on its own, it is absolutely crucial that you obtain it via nutritional sources in your diet.
Where Does DHA Come From?

Seafood is one of the leading sources of DHA, though beef and eggs have a good amount of it as well. Here are a few of the richest sources:
- Mackerel
- Salmon
- Herring
- Sardines
- Oysters
- Scallops
- Caviar
- Cod
- Tuna
- Sea bass
- Cod liver oil
- Eggs
- Grass-fed beef
What Does DHA Do?
DHA plays a critical role in the development and functioning of your brain. It lives within the membranes of cells, helping them communicate with one another. (2) This is particularly important for nerve cells in the brain. Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are designed to help cells stimulate and communicate with each other.
This fluidity of nerve cells can benefit the entire body. When you have a healthy amount of DHA, your body can fight inflammation and lower blood triglycerides, among other important functions.
The Top 5 Benefits of DHA

1. Boosts Brain Development in Children
DHA is necessary for proper brain development in children. That’s because the frontal lobes of the brain, or the part responsible for cognitive skills like memory, are dependent on DHA during growth and development. (3)
Unfortunately, the average intake of DHA is rather low in children and toddlers since they don’t typically eat much fatty fish. A diet lacking these types of healthy fats could lead to learning disabilities such as ADHD, dyslexia, dyspraxia and other behavioral disorders. (4)
Luckily, supplementation can help. Studies show that children’s behavior and cognition improves when their diets were supplemented with doses of DHA and other polyunsaturated fatty acids. (5)
2. Decreases Risk of Alzheimer’s
As we get older, our brains battle cell damage, oxidative stress and memory decline. Getting enough DHA can help ensure that your brain has the energy it needs to fight off the damage from oxidative stress.
If you’re not getting enough DHA, your risk for cognitive decline increases. Getting enough DHA can prevent Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders. (6)
3. Improves Vision
DHA plays a key role in healthy vision as well. This is because DHA activates rhodopsin, a membrane protein within the rods of the eye. (7) Rhodopsin is found in specialized cells called rods, which sit in the retina to increase low light vision. When you get enough DHA, your brain can more readily receive the messages your eyes are trying to send.
4. Reduces Inflammation
When we experience inflammation, it’s because immune cells called macrophages are triggered. A process called autophagy determines whether these cells are calm or hyperactive. (8)
Omega-3 fatty acids, and DHA in particular, inhibit the secretion of inflammatory factors that would otherwise be caused by macrophages.
It’s important to get enough DHA to keep inflammation down, which in turn decreases risk of autoimmune disease as well as swelling and pain in joints. (9, 10)
5. Improves Heart Health
Your heart health is also dependent upon DHA. The anti-inflammatory properties of DHA can help reduce the risk of blood clotting and lower blood pressure, and may even reduce blood triglycerides. (11) Some issues associated with high triglycerides include diabetes, high blood pressure and obesity.
Should You Supplement with DHA?
If you’re eating a healthy serving of wild-caught fish a few times per week, chances are you have no need to supplement. If you aren’t a fan of fish, you have a few options for supplementation.
Fish oil is one of the most widely available options. It comes from fatty fish and contains two main omega-3’s: DHA and EPA. You can also use krill oil, which is extracted from small shrimp-like crustaceans from Antarctica.
Green-lipped mussel extract, made from a type mussel found in New Zealand, might be the best option, as it also contains a rare fatty acid with powerful antioxidants. The combination of the fatty acids in green-lipped mussel extract isn’t found in any other marine oil, making it one of a kind. (12)
The recommended daily dose for DHA supplementation is around 250 milligrams/day, but there’s no big concern of overdoing it – high doses are easily tolerated. (13)
The Bottom Line
If you’re looking to boost your cognition, lower inflammation, and improve your vision, you might benefit from adding some DHA into your diet. Seafood, grass-fed beef and eggs are good sources of DHA, and can contribute to a healthy heart and brain.
Read This Next: 6 Natural Ways to Boost Your Brain Power



 Turkey and Mashed Sweet Potato Balls
Turkey and Mashed Sweet Potato Balls




Show Comments